Modelling of excitable cells - the EMI model#
The Extra, Intral Membrane (EMI) model is a way of modelling the intracellular, extracellular and membrane between the two explicitly. A full introduction to the topic is given in [TMR21].
In this section, we limit ourselves two the following set of equations, with a single intra-cellular and extracellular space.
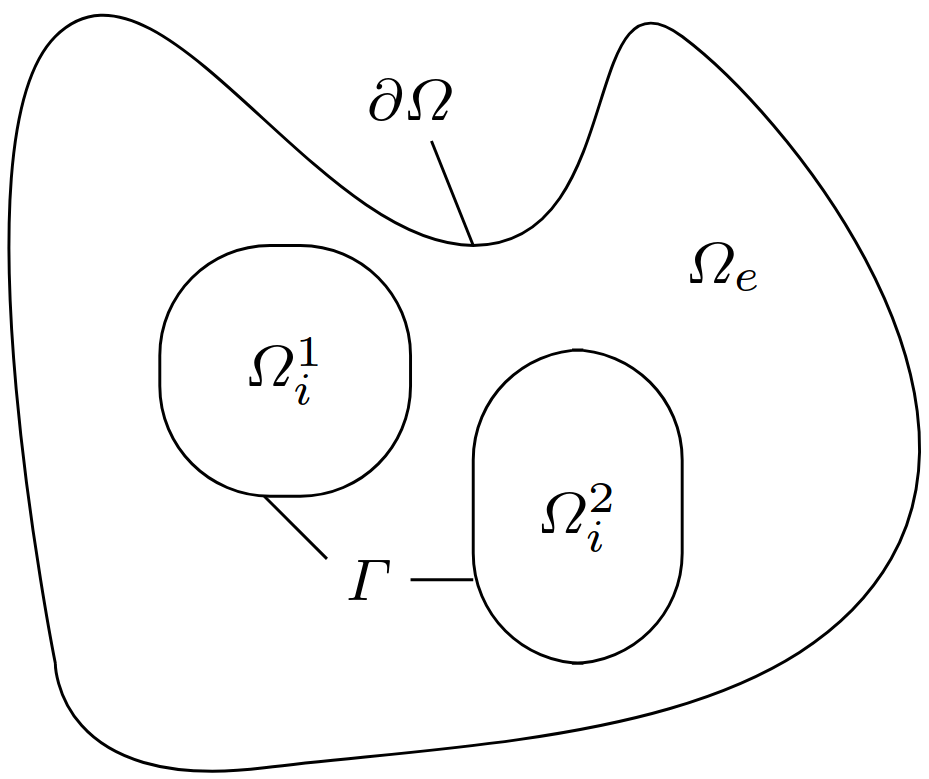
Fig. 1 Illustration of the intracellular and extracellular space. Figure is from [BFRSC24] and is under the creative commons license.#
Implementations#
With the fem, there are two classical ways of modelling Poisson-like equations, namely the primal and mixed formulation. However, as the EMI problem can be thought of as two Poisson problems with a specific coupling condition, it expands the number of possible discretizations to four [KMR21]:
References#
Pietro Benedusi, Paola Ferrari, Marie E. Rognes, and Stefano Serra-Capizzano. Modeling excitable cells with the emi equations: spectral analysis and iterative solution strategy. Journal of Scientific Computing, 98(3):58, Feb 2024. doi:10.1007/s10915-023-02449-2.
Miroslav Kuchta, Kent-André Mardal, and Marie E. Rognes. Solving the EMI Equations using Finite Element Methods, pages 56–69. Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2021. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-61157-6_5.
Aslak Tveito, Kent-Andre Mardal, and Marie E. Rognes, editors. Modeling Excitable Tissue: The EMI Framework. Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2021. ISBN 978-3-030-61157-6. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-61157-6.